Putting the tracks on a satellite image.
I had my handheld GPS (a Garmin GPSmap 60c) running while I was drying cherries and the GPS tracked my movements. Today, on a whim, I saved the tracklogs and downloaded them to my Mac. Then I brought them into Google Earth and looked at a few of the orchards.
The tracks are not very accurate. They show a zig-zag motion that appears to cross diagonally across the rows. In reality, when I reached the end of each row, I moved to the side and turned to go down another row. So rather than pointed endings and diagonal tracks, an accurate rendering would show squared off endings and parallel tracks.
But I still think it’s interesting to see how I moved over the land. Take a look and see for yourself. These are the tracks from my flights on July 4.
In this first example, I’d flown past the orchard on the south side from west to east, then circled back. I made a wide clockwise circle of the orchard to get my bearings, then came in on the south end, near a white single-wide mobile home. There was a woman there, waving happily when I arrived. She’d left the door of her house open and I blew a bunch of leaves into it. (Oops.) My track took me back and forth up the triangular orchard. Although the track makes it look as if I had a short row near the top, it’s just another inaccuracy in the track. I departed the area with a clockwise circle to the west.
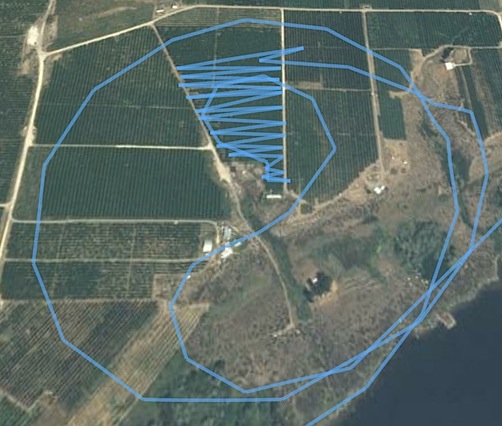
Here are two others representing three dries. I went to the lower one first, passing it by on the south from west to east. I circled back, then came in on the southwest corner. I went back and forth from west to east, then broke off. It started to rain so I repositioned to the airport, which was less than a mile away. I read for a while, then got a call with a new list of orchards. I started back up and took off, returning to re-dry the lower orchard in this image again (hence the double set of track lines) after doing others a bit farther to the west. I did the upper orchard about an hour later, coming in from the northwest and departing from the southeast side back to the west.
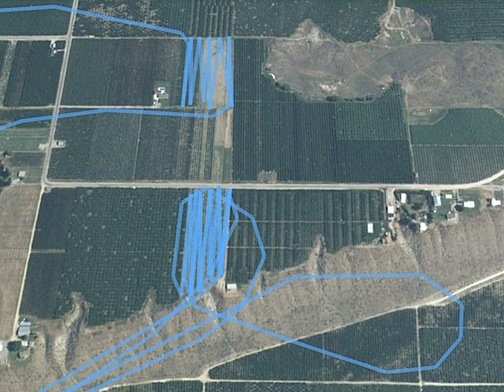
Here’s a sloppy looking one that really wasn’t this sloppy. I did the lower orchard first, coming in from the southeast and departing out the northwest. I then went directly to the upper orchard, beginning the dry at the southwest and exiting at the northwest. The pair of diagonal lines going across the bottom of this screenshot represent overflights of the orchard on my way to or from the ones in the previous screenshot.
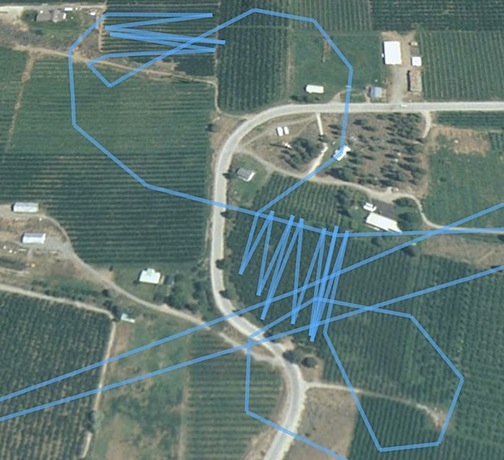
This is the first orchard I described in some detail in my “I Dry Cherries” post. Again, I really didn’t fly a zig-zag pattern in the main orchard. and I’m certain I flew at least two more rows (one in each direction) in the smaller orchard. But the GPS doesn’t seem to pick up all the points when it makes its tracks. The two other straight lines near the bottom right of the image are overflights to/from other orchards. That’s the Columbia River/Lake Pateros in the bottom right corner of the shot.
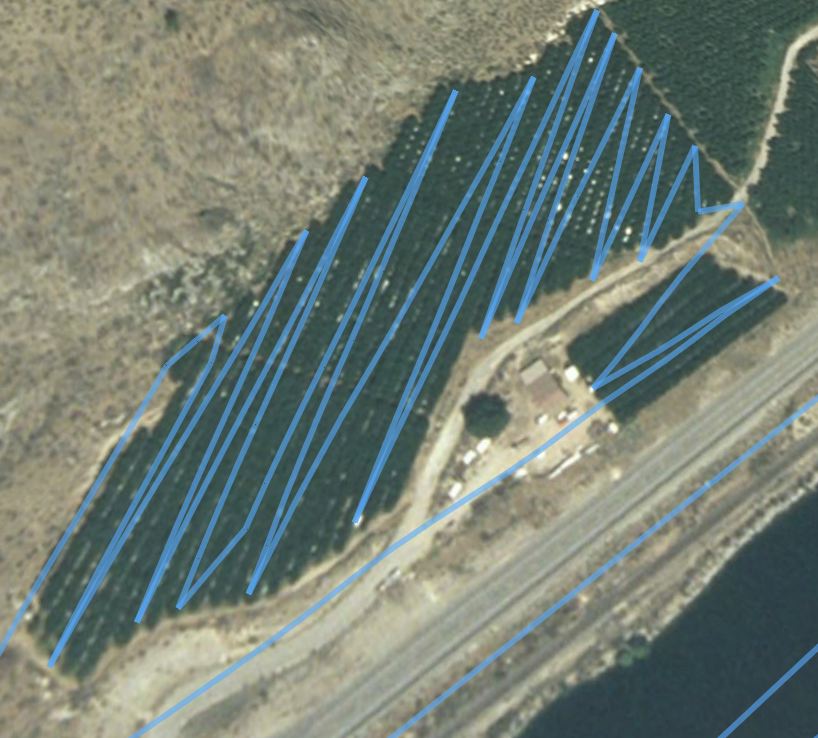

These are just a few of the orchards. You get the idea. Next time I fly, I’ll use my new geotagger. It can save up to 600,000 waypoints (I think) so I have a feeling the pictures it draws will be a lot more accurate. If they are, I’ll show them off here again.
We all know what a geek I can be.

 So now you’ve got 1,000 hours of PIC time, accumulated over a period of about 2 to 3 years. You’re ready for a “real” job. Fly tours at the Grand Canyon (like I did). It’s great experience, but the pay is only slightly better than what a CFI gets. Fly in the Gulf of Mexico, bringing oil rig workers and VIPs to and from platforms on a featureless, watery landscape, miles from land, in good and bad weather. More good experience, slightly better pay. Pretty crappy living conditions, from what I hear. And I don’t think many women work out there. (Would love to hear from a woman who does; use the Comments link.)
So now you’ve got 1,000 hours of PIC time, accumulated over a period of about 2 to 3 years. You’re ready for a “real” job. Fly tours at the Grand Canyon (like I did). It’s great experience, but the pay is only slightly better than what a CFI gets. Fly in the Gulf of Mexico, bringing oil rig workers and VIPs to and from platforms on a featureless, watery landscape, miles from land, in good and bad weather. More good experience, slightly better pay. Pretty crappy living conditions, from what I hear. And I don’t think many women work out there. (Would love to hear from a woman who does; use the Comments link.)