Initial thoughts about my new flight following solution.
My friend, Jim, is an Idaho-based R44 pilot with a company very similar to mine. He’s a single pilot Part 135 tour and charter operator who sometimes operates over very remote terrain.
Of Flight Plans and Flight Following
One of the challenges we face as charter operators is last-minute route changes requested by paying passengers. For example, suppose the passenger books a flight from Scottsdale to Sedona. I’m required by the FAA to file a flight plan that indicates my route so that if we don’t turn up in Sedona, they’ll know which way we went and can [hopefully] find us. But at times — sometimes after the flight is already under way — the passenger might say something like, “Can you follow the course of the Verde River to Camp Verde?” This is not the most direct route and it’s not likely to be the one I planned. But what do I do? Say no?
[The right answer is yes, say no. That’s the answer the FAA wants to hear. But the FAA is not paying by the hour to conduct the flight. The FAA is not going to refer its friends to a friendly, accommodating pilot.]
The problem is, if I deviate from a route and something goes wrong, the search teams may not be looking for us anywhere near where we are. So they might not find us. And sure, I have an ELT (emergency locator transmitter) in my aircraft — even though it is not required by the FAA. But how well do those really work? It certainly didn’t help them find a pilot and his co-worker when they literally disappeared on a flight between Deer Valley in North Phoenix and Sedona nearly two years ago. They’re still missing.
And then there’s Steve Fossett. Or maybe I should have said, where’s Steve Fossett. They must have spent millions by now to find him and he’s still among the missing.
Airplane pilots and pilots flying in the flatlands of the midwest can request something called flight following from the flight service station (FSS). Flight following keeps you on radar so they pretty much always know where you are. The problem with helicopters is that we fly so darn low. Even if I flew up in nose bleed territory at, say, 1500 feet above ground level (AGL), the terrain in the area I fly is too mountainous to keep me on radar. I’d have to fly much higher to stay on radar. And if I’m going to be that high, I may as well fly a plane. So flight following is not a practical solution.
The True Geek’s Solution
Jim also flies in remote and often mountainous areas. And, like me, he’s a true gadget lover — someone who likes to fiddle with electronic toys. (I think he’s lusting for a POV.1 after seeing mine.) He was based in Chelan for cherry drying season and happened to see the SPOT Messenger displayed at the local Radio Shack. He went in and checked it out. Then he did more homework. Then he bought one and told me about it.
 The SPOT Satellite Messenger is a personal location device. It’s about the size of my Palm Treo and, as you can see here, bright orange so it’s easy to…well, spot.
The SPOT Satellite Messenger is a personal location device. It’s about the size of my Palm Treo and, as you can see here, bright orange so it’s easy to…well, spot.
My understanding of the unit is that it combines GPS receiver technology with satellite transmitter technology. So you turn it on and it acquires its position via GPS. You can then use one of four different features, depending on the subscription plan you choose:
- The SPOT standard service plan, which costs $99/year, includes the following three features:
- OK sends a text message or e-mail message to the phone numbers or e-mail addresses you specify. The message, which is customizable, tells the people on the list that you’re checking in OK and provides the GPS coordinates for your position. Those coordinates include a link that, when clicked, displays your position on Google Maps.
- Help, is similar, but it sends a customizable help message to the people you specify. The idea here is that you need help and have no other way to contact someone who can help you.
- 911 sends your GPS coordinates to the folks at the GEOS International Emergency Response Center, who, in turn, notify the appropriate emergency authorities. This is for real, life-threatening emergencies. The Response Center folks also contact, by phone, the two people you specify to notify them of the signal.
- The tracking upgrade option, which costs another $49/year, includes live tracking, which, when activated, sends you GPS position every 10 minutes or so to the SPOT folks. This information is visible to anyone who has been given access to a Share page you configure with or without a password.
Jim went with both plans. When I bought mine on Monday, I did the same.
First Thoughts
I’ve been playing with SPOT on and off since Tuesday morning. In general, I like it and I think it’ll do the job I intend to use it for — flight following on those long cross-country flights.
After configuring message recipients, I started out by sending a few OK messages. Although the marketing material makes it seem as if those messages are instantaneous, they’re not. After pushing the OK button, the unit will try for up to 20 minutes to send your OK location via satellite uplink. It’ll send the message 3 times, but only one message is forwarded to the people on your list. For experimental purposes, I made myself one of those people. I had to wait longer than 20 minutes to receive one or two of the messages. To be fair, part of the reason for that could be my location at the time — flying between Wenatchee and Seattle in mountainous terrain. (I don’t think my cell phone was receiving very well.) The delay is satisfactory, once you realize that it’s not an instant communication.
For obvious reasons, I have not used Help or 911 yet. Let’s hope I never have to.
I did set up tracking. It took several tries to turn it on properly. The unit does not have a screen, so you have to rely on understanding the blinking lights to know what it’s doing — if anything. Twice I thought I was enabling tracking, but discovered that all I did was send OK messages. Once, tracking was on and in trying to turn it on, I really turned it off. In all cases, it was operator error. Evidently, you cannot turn on tracking during the 20-minute period in which an OK message is being sent. Since both features use the same button, it’s pretty easy to do one thing instead of the other if you don’t pay attention to how long you hold down the darn button.
My husband complained that the messages he received did not include the date and time. We later realized that it was because he was not viewing the message on his phone; he was viewing its summary. (My husband is text message challenged.)

 The e-mail version of the OK message is handy because of the link it includes. Click it and go right to Google Maps with the position clearly marked. Here are two examples. In the first one, we’re flying just to the east of Snowqualmie Pass over I-90. In the second one, we’re sitting on Pad 6 at Boeing Field in Seattle. These images are at two different magnifications. All GoogleMaps features work — it’s just the location put into GoogleMaps. My personal Messages page on the FindMeSpot.com Web site displays all points with the option of displaying any combination of them on Google Maps. It also enables me to download these points to a GPX or KML format file for use with a GPS receiver or GoogleEarth.
The e-mail version of the OK message is handy because of the link it includes. Click it and go right to Google Maps with the position clearly marked. Here are two examples. In the first one, we’re flying just to the east of Snowqualmie Pass over I-90. In the second one, we’re sitting on Pad 6 at Boeing Field in Seattle. These images are at two different magnifications. All GoogleMaps features work — it’s just the location put into GoogleMaps. My personal Messages page on the FindMeSpot.com Web site displays all points with the option of displaying any combination of them on Google Maps. It also enables me to download these points to a GPX or KML format file for use with a GPS receiver or GoogleEarth.
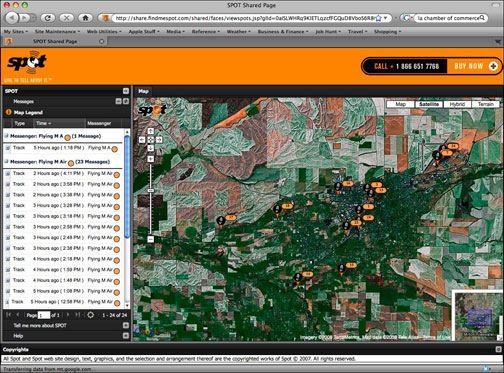
The Share page feature, which is still in beta, was not working when I first tried it. But it’s working now — and quite well! I set up a page that does not require a password so anyone could check in and see where I was when I was traveling with SPOT tracking turned on. Apparently, it only shows the past 24 hours of activity, so it you’re checking it now and there’s nothing going on, it’s because I’m not traveling with SPOT. But here’s what it looks like right now; as you can see, I spent a lot of time exploring Walla Walla, WA today:

A few things about this feature:
- The lines between the points (which, for some reason, are not showing up in the screenshot) do not represent tracks. I was in a truck today and did stay on roads.
- If the unit did not have a clear shot of the sky, the point that should have been recorded wasn’t. This wasn’t a problem today, since I had the unit sitting on the dashboard in the broiling sun — partially to see if heat would affect it. (It didn’t.)
- Clicking a point in the list on the left side “flashes” that point in the display. You can also click other controls to get more information.
- If you leave this page open, it will automatically update. So you can watch new points appear if you’re tracking someone. Way cool.
The URL for this feature is long and impossible to remember, so I created a custom URL using TinyURL: http://www.tinyurl.com/FindMaria. I invite you to try it for yourself.
Overall
My overall opinion is very positive. It will certainly give me peace of mind while flying in some of the remote desert locations I fly in. I think it’s worth the $150 unit cost plus annual subscriptions.
Even if something goes terribly wrong out there, I want to be found.
My next challenge: getting it to send OK messages to my Twitter account. Anyone have any ideas?
 I just watched Bill Maher’s documentary, Religulous. It’s been in my Netflix queue for some time now and I recently let it ride to the top. I watched it on my second monitor while doing some relatively mindless work on the other.
I just watched Bill Maher’s documentary, Religulous. It’s been in my Netflix queue for some time now and I recently let it ride to the top. I watched it on my second monitor while doing some relatively mindless work on the other.
 The other night, I watched Welcome to Macintosh, a new documentary by filmmakers Robert Baca and Josh RIzzo.
The other night, I watched Welcome to Macintosh, a new documentary by filmmakers Robert Baca and Josh RIzzo. The
The 
 The e-mail version of the OK message is handy because of the link it includes. Click it and go right to Google Maps with the position clearly marked. Here are two examples. In the first one, we’re flying just to the east of Snowqualmie Pass over I-90. In the second one, we’re sitting on Pad 6 at Boeing Field in Seattle. These images are at two different magnifications. All GoogleMaps features work — it’s just the location put into GoogleMaps. My personal Messages page on the FindMeSpot.com Web site displays all points with the option of displaying any combination of them on Google Maps. It also enables me to download these points to a GPX or KML format file for use with a GPS receiver or GoogleEarth.
The e-mail version of the OK message is handy because of the link it includes. Click it and go right to Google Maps with the position clearly marked. Here are two examples. In the first one, we’re flying just to the east of Snowqualmie Pass over I-90. In the second one, we’re sitting on Pad 6 at Boeing Field in Seattle. These images are at two different magnifications. All GoogleMaps features work — it’s just the location put into GoogleMaps. My personal Messages page on the FindMeSpot.com Web site displays all points with the option of displaying any combination of them on Google Maps. It also enables me to download these points to a GPX or KML format file for use with a GPS receiver or GoogleEarth.