What it’s really like.
Help Wanted!I wrote this blog post way back in 2009. Since then, I’ve built a medium sized cherry drying business and have moved to the Wenatchee area to be close to my work. Each summer, I contract with five or more pilots to fly with me and help me cover my contracts. If you have an R44 helicopter and want a “paid vacation” in central Washington State next summer, I want to hear from you. Read this and then get in touch.
I’ve been writing a lot about my summer gig as a cherry drying pilot. Most folks focus on the flying or the money or the simple fact that I can perform what looks like an easy task, make money, and build flight time. Few people seem interested in what it’s really like.
The truth is, it’s neither fun nor glamorous. In fact, when you look at the big picture and understand the responsibility and potential danger involved, it’s rather tedious.
So I thought I’d take the time to fully describe what being a cherry drying pilot is all about.
An Introduction to Cherry Drying
Let me begin by describing what this is all about.
Cherries grow on trees in orchard blocks in the U.S. northwest (and elsewhere). Like other fruit trees, cherry trees flower in the spring and are pollinated by birds and bees and possibly by other methods I’m not familiar with. The fruits begin to grow.
 About three weeks before the cherries are ready to be picked, they are particularly vulnerable to threats that can damage them. One of those threats is water. When it rains, the water sticks to the cherries and can cause them to rot, split, or both. This makes the cherries far less valuable to buyers.
About three weeks before the cherries are ready to be picked, they are particularly vulnerable to threats that can damage them. One of those threats is water. When it rains, the water sticks to the cherries and can cause them to rot, split, or both. This makes the cherries far less valuable to buyers.
Cherry growers have long tried to find ways to dry the cherries and prevent the rot/split problems. They put fans on tall poles in their orchards and run blowers up and down the rows. But this isn’t usually effective. Enough rain in those last few weeks can destroy the entire crop.
Sometime in the past — maybe 10 or 15 years ago? — someone had the idea of using the downwash of helicopters hovering over the cherry trees to blow the branches around and shake the water off the cherries. This was extremely effective and apparently well worth the cost.
“Cherry drying” by helicopter was born.
How I Got Here
Learn more about helicopter cherry drying I first heard about cherry drying a little over four years ago. I was looking for summer work with my helicopter and another helicopter pilot, who was based in Seattle, got in touch with me. He was trying to build a cherry-drying operation and wanted to get together a bunch of pilots he could call on each year.
Two years in a row, I almost got work doing this. But there wasn’t enough guaranteed work for me to make the 10-hour (each way) ferry flight from Arizona. Last year, there was. I flew up, stopped in Portland, OR to get some training with another pilot, and set up base in Quincy, WA. I was working for my pilot friend as a subcontractor for several growers and for another cherry drying provider.
Last year wasn’t very good for pilots — but it was great for growers. Why? It didn’t rain. I was on a variety of contracts for a total of seven weeks and only flew 5.2 hours. And because my assigned orchard blocks were so small, most of that time was spent flying from one to another.
This year, everything was a mess. My friend had let his business go because of a serious health problem so he wasn’t digging up work for me. The other cherry drying provider had promised me some work but, at the last possible minute, went out of business. Pilots like me were frantic, trying to find contracts for work. Growers were frantic, trying to find pilots. And out of this mess, with the help of some contacts I had from last year, I managed to get four contracts stretching out over a period of six weeks.
How It Works
The cherry drying work I do is on contract. This year, I contracted directly with growers (or orchard managers) for a 2 or 3 week period. During the contract period, the grower pays me a daily standby fee. Payment of this fee ensures that I will be available to come dry the orchard block within a reasonable period of time — usually within 20 minutes of the call to come.
When it rains, the grower calls. He usually calls at least twice:
- The first call is what I call the “heads up” call. At this point, it’s either raining or very likely to rain on the orchard. The grower wants to make sure I’m aware that I’ll probably be called out to dry soon.
- The second call is the call to action. The grower expects me to arrive as quickly as possible and get right to work.
When I’m finished drying and return to my base, I note the time flown as indicated on my Hobbs meter. At the end of the week, I bill the grower for the flight time at a pre-agreed hourly rate.
The Expenses
Because I can never depend on it to rain, I have to set my standby rate high enough to cover all of my fixed expenses. These expenses include:
- Cost of transporting the helicopter between Arizona (where I live) and Washington (where I dry cherries).
- Cost of getting my truck up to Washington and back.
- Lodging expenses for the entire time; I save money by living in my small RV, which I tow up with my truck.
- Meals and other living expenses.
- Insurance. Last year I had to supplement my regular insurance with a second policy; this year I got a policy that covers all of my operations.
There are also a bunch of startup costs that have to be considered:
- Helicopter. Medium sized helicopters with two-bladed systems are best. Think Robinson R44, Bell JetRanger, and Hiller. R22s and Schweitzer 300s generally don’t push enough air, although they can get into tighter spots.
- Truck. It’s needed to provide ground transportation and haul around fuel.
- 100-gallon fuel tank, pump, filter, and grounding strap so I can carry and pump aircraft fuel.
- Helicopter helmet.
- Nomex flight Suit.
As you can imagine, this can be a major investment. My fuel setup alone cost $2K. And have you priced up helicopter helmets lately?
Finally, the expense many people don’t consider: taking a normally revenue-generating helicopter offline.
You see, when you contract for cherry drying, you have to keep your helicopter near the orchards. That means you can’t hold it out for hire on other jobs. While my helicopter is here in Washington, I can’t be doing charter work down in Arizona. I have no customer base here. And even if I did, I couldn’t fly customers unless I was absolutely certain it wasn’t going to rain.
So suppose I’d fly 5 hours a week in Phoenix but can’t fly those 5 hours in Washington. That’s 5 hours of revenue lost each week. My standby rate has to compensate me for this potential loss of revenue.
What It’s Like
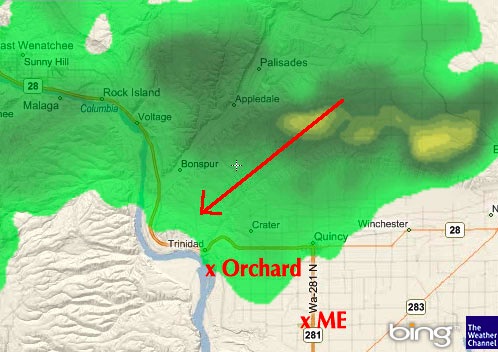
Cherry drying is a waiting game, one that turns you into a local weather expert.

Here’s the kind of analysis I make all day long when there’s weather moving in. The arrow indicates the direction of the weather movement.
Each day starts with a look out the window and at the current day’s weather. I have an Internet connection here, so I can check the weather from a variety of sources throughout the day. I also have a scanner with weather frequencies that broadcast official local weather 24 hours a day. If there’s no rain in the forecast and no clouds in the sky — like most days last season — you’re free to do what you like, as long as you keep monitoring the weather and can be back at base at the slightest hint of rain. But if there’s any rain in the forecast or any clouds in the sky, you need to stick around base, just in case those clouds turn rain-bearing and they drop moisture on your assigned orchard blocks.
Or maybe the day starts with a phone call. Like today.
The point is, when you’re on contract and being paid standby money, you’re responsible for making sure you’re available quickly when called. That means you can’t screw around and do whatever you want wherever you want. If it looks like rain, you need to be ready to fly. Even if it doesn’t rain and you don’t get the call.
For me, that means spending a lot of time hanging around my RV at the golf course. (It’s almost unfortunate that I don’t golf.) It means having access to weather information and having something to do to keep busy so you don’t die of boredom. It means keeping your cell phone fully charged and in a place where it gets a good signal.
It doesn’t mean disappearing to Seattle for a few days without telling anyone. That’s a horror story I heard from a guy who hires pilots as subcontractors. He’d hired one irresponsible pilot who didn’t take the job seriously. When he called the guy to fly, the guy admitted that he was in Seattle and couldn’t get back for hours. That’s too late. The crop would be destroyed by then.
For the amount of money we’re being paid to hang around, the least we could do is hang around.
Oh, and did I mention how long the days are here up in North Central Washington in June and July? Sunrise is at around 5 AM. Sunset is around 9 PM. I have to be available for all daylight hours. That means I have a 17-hour work day.
The Work
Of course, sooner or later those calls will come.
On the first call, I prepare the helicopter and myself for flight. For the helicopter, that means taking off the cockpit cover (if it’s on). I’ll also remove the blade tie-downs, but only if a storm isn’t approaching my position. The helicopter is already pre-flighted. Then I’ll go back to the camper — it’s literally right down the block — and prep myself by pulling on my flight suit. I wear a tank top with it, so I can keep the top half of the flight suit off with the sleeves tied around my waist. It’s hot and humid here and I don’t want to sweat my brains out in a long-sleeved Nomex suit. I make sure all my documents and my sunglasses and the helicopter keys are in my pockets. I put on socks and comfortable shoes. If Alex the bird is outside, I bring him in. I also zip the bed windows closed so rain doesn’t get into the camper. I put a bottle of regular water and a bottle of “vitamin water” in my little six-pack cooler to bring along on the flight.
And then I wait.
The other day, I waited three hours. The second call never came. The first call had been premature and it never rained on the orchard. I had to call the grower to see if he thought he’d need me to fly. He didn’t. I was all dressed up with no place to go.
When the second call comes, I’m ready to go. I pull up the top half of my flight suit and zip up. I lock up the camper and drive back over to the helicopter. I take off the tie-downs (if they’re not already off), do a walk-around, and climb on board. I start the engine and get it warming up. Then I put on my helmet, set up my cell phone to receive calls in flight, and when the helicopter is warmed up, I take off.

I thank my lucky stars that I never had to dry this nightmarish block.
I use my GPS to fly direct to the orchard block. I’ve already scouted all the blocks on foot and by air, so I know how to approach. I come in low over one corner and settle down to 5 to 10 feet over the tree tops. Then I fly slowly down the row. At the end, I turn, move over a row or two — depending on the density of the trees — and fly back to the side I started on. I go back and forth like this at 5 to 10 knots groundspeed, being careful to avoid obstructions like wires, fans, poles, tall bordering trees, hillside rock outcroppings, and buildings. Some orchard blocks are easy to dry. Others are damn near impossible. Most fall somewhere in between — not too difficult to do, but not so easy that you can do it without paying attention.
Complacency can kill you — or at least destroy your helicopter and a bunch of trees.
You can read about my first time drying here.
Cherry Drying Isn’t for Everyone
I can’t tell you how many people have contacted me, asking me to help them get into cherry drying. Do these people understand the expenses involved? The skill level required? The dedication to waiting around for a phone call that may never come? I don’t think so.
I also don’t think they understand the competitive nature of this work. Right now, there are too many pilots for the available work. We’re all competing against each other for contracts. This year, a bunch of JetRanger pilots were so desperate for work that they undercut the rates of most other pilots — they were actually billing themselves out for less than R44s! How can we compete against that?
When the company I flew for part of the season last year fell apart this year, I had to scramble to get the contracts I have. While I got enough work for myself, I could handle more. It’s just tough to break into this work and build a reputation for yourself — especially if you don’t get a chance to fly and prove you can meet growers’ needs. I wasn’t able to prove myself last year and feel lucky to have the opportunity again this year.
And then there’s the skill level required to do this kind of flying. It’s not as easy as it seems — especially if conditions are less than perfect. Sure, any decent pilot should be able to hover slowly over tree tops. But for hours on end? And what if the wind kicks up and you’re dealing with a quartering tailwind as you travel in one direction? Or the block is full of obstructions, like power lines and fan poles? Or bordered by trees? Or there are storms in the area that you need to fly through to reach your orchard blocks?
Why do you think I wear a helmet and a Nomex flight suit when I fly?
No Flying Today
I worked on this blog post on and off all day. I watched the storm clouds build and move in the sky and on Doppler radar. I saw the scary yellow blobs of convective activity flare up and fade out on my computer screen.
It’s still cloudy, but if the radar can be believed, it’s not threatening rain over my orchard.
But it’s only 5 PM. There are still more than 4 hours left in my work day.

 Robinson Helicopter Company recommends that all pilots — and even passengers! — wear flight suits. Safety Notice 40 was released in July 2006, possibly in response to an accident with a post-crash fire in Texas. Robinson often releases Safety Notices in response to what it sees as dangerous or potentially dangerous situations. Safety Notices are not requirements; they’re suggestions. They’re also Robinson’s way of “covering its butt.” The company is owned by Frank Robinson and is self-insured. By recommending that we wear flight suits, Robinson Helicopter cannot be held accountable for burn injuries if we’re not following their recommendation.
Robinson Helicopter Company recommends that all pilots — and even passengers! — wear flight suits. Safety Notice 40 was released in July 2006, possibly in response to an accident with a post-crash fire in Texas. Robinson often releases Safety Notices in response to what it sees as dangerous or potentially dangerous situations. Safety Notices are not requirements; they’re suggestions. They’re also Robinson’s way of “covering its butt.” The company is owned by Frank Robinson and is self-insured. By recommending that we wear flight suits, Robinson Helicopter cannot be held accountable for burn injuries if we’re not following their recommendation.

 Looking at the camera today, it’s amazingly big and clunky. But it takes a decent picture — certainly good enough for my time-lapse experiments. And frankly, I was having trouble getting my mind around leaving my Nikon outdoors, unattended, for hours at a time. It could be because the tripod got knocked over once and it was sheer luck that it fell toward a rail that caught it rather than toward the empty concrete behind it. I had no love for the G5; if it broke, well, that’s the way it goes. Ditto if it got stolen. In fact, I’d be more upset about losing my tripod or
Looking at the camera today, it’s amazingly big and clunky. But it takes a decent picture — certainly good enough for my time-lapse experiments. And frankly, I was having trouble getting my mind around leaving my Nikon outdoors, unattended, for hours at a time. It could be because the tripod got knocked over once and it was sheer luck that it fell toward a rail that caught it rather than toward the empty concrete behind it. I had no love for the G5; if it broke, well, that’s the way it goes. Ditto if it got stolen. In fact, I’d be more upset about losing my tripod or  About three weeks before the cherries are ready to be picked, they are particularly vulnerable to threats that can damage them. One of those threats is water. When it rains, the water sticks to the cherries and can cause them to rot, split, or both. This makes the cherries far less valuable to buyers.
About three weeks before the cherries are ready to be picked, they are particularly vulnerable to threats that can damage them. One of those threats is water. When it rains, the water sticks to the cherries and can cause them to rot, split, or both. This makes the cherries far less valuable to buyers.