Two flights, two hours.
I’ve been on contract for cherry drying services since May 26. It’s the earliest contract start I’ve ever had.
Although the first orchard I was on contract for dodged a few storms right at the beginning of the contract, the weather settled down and was very nice for two full weeks. Too nice, if you ask me. The east side of the Cascade Mountains is almost as dry a desert as the one I left in Arizona.
During that time, two other small orchards came on contract, giving me responsibility for three orchards totaling 60 acres. The only drawback is that 30 acres are in Quincy, about 10 miles from my home in Malaga, where the other 30 acres is. So there’s a bit of uncompensated flight time between orchards.
I’m Ready for the Calls
With a 20% chance of rain in the forecast for Thursday, a few growers — including one who isn’t on contract yet — called to check in. Normally, I don’t bug my growers unless they owe me paperwork or money; when there’s a chance of rain, they sometimes call just to make sure I’m really around.
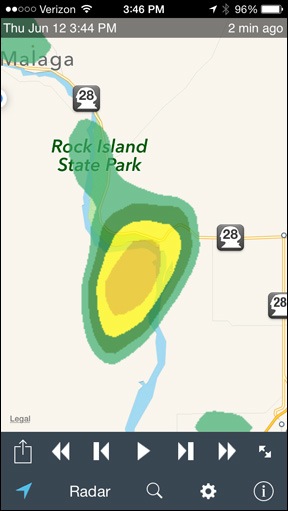
What they don’t realize is that from the first day of my first contract to the last day of my last contract, I’m walking weather advisory service. I know the chance of rain for the next 3 days (50% today, 20% tonight, 0% Saturday and Sunday, 20% Monday) and what’s on radar now (dissipating storm system headed for Quincy orchard and building storm system heading for Malaga, both from north in counter-clockwise rotating weather pattern). I have weather on my phone, iPad, and computer and always have at least one of them within arm’s reach.

Rain in the area? I know about it and am ready to fly.
While under contract, I’m never more than an hour away from my helicopter, even on nice days with no chance of rain. If there’s rain in the forecast, I’m never more than 30 minutes away. If there’s any chance at all of rain within the next 30 minutes, I’m hanging out with the helicopter. If it’s raining on any of my orchards, I’m suited up and the helicopter is preflighted, untied, and ready to go. No matter what the weather is, I don’t drink — not even a glass of wine with dinner — during daylight hours. Of course, by the time the sun goes down, I don’t feel like that glass of wine anyway.
As for the helicopter, it’s completely up-to-date on all maintenance that would have it down for more than a few hours. Both fuel tanks are topped off — I refuel after every flight — giving me an endurance of at least 3 hours over the trees. I have the hinge pins off the pilot door so I can pull the door quickly — I’ve discovered that it’s better to fly with the door off, especially if it might get sunny during a flight; I’d rather be a little wet than roasting in the sun.
Thursday’s Flights

There’s always something to do with a home under construction.
With a 30% chance of rain forecasted for Thursday, I hung out at home, which is where my helicopter is now based. The builders were still working on on my building and I had plenty to do to keep busy.
By around 1 PM, it started clouding up. I watched various storms on the radar, including a nasty cell near Peshastin and another near Cashmere. But all the storms were moving south to north and both of those points were west of me and my orchards. No threat. Still, I spent some time getting scrap lumber I planned to use for projects stowed away under my RV and closing up the windows in my Jeep and truck.
When I saw a storm come out of nowhere and apparently drop a ton of rain right on top of one of my orchards — which I could see from my home — I suited up and went out to prep the helicopter.
When the call came, I was actually sitting in the helicopter with the key in the ignition. I told the grower I’d be over as soon as I could. I was hovering over his orchard less than 10 minutes later.
I don’t particularly care for this orchard. In 23 acres, they’ve managed to throw in a cornucopia of obstacles: 4 buildings, 2 sets of wires (plus a nearly invisible one running from a pole to a house right at treetop level), 3 wind machines, a bird house, tall border trees, and a pipe that, for some reason rises about 5 feet over the tops of the cherry trees beneath it. It was just after negotiating around this pipe that my main rotor blades trimmed some narrow branches on one of the border trees.
And then there was the wind. Dead calm one minute and gusting like crazy the next. I made a 180° turn at the end of a row of trees and got a headwind gust that lifted me 30 feet. Sheesh.
It takes about 45 minutes to dry this orchard and I was glad when I was done. I sped over to the airport, parked at the fuel island, and topped off both tanks. My client called while I was at the airport to thank me for my speedy response. I told him I hoped I could respond that quickly every time he called and reminded him that I lived less than two minutes away by air.
After refueling, assuming I was done for the day, I headed home.

The fuel island at Wenatchee Pangborn on a rainy day. My home is at the base of the cliffs behind the helicopter’s tail rotor in this photo.

It should not have been a surprise to get a call from my Quincy client, considering this storm cell passed right over his orchard.
I was home less than a hour when a call came from the owner of my Quincy orchard. I felt sorry for the guy — he was going to start picking the next day. He’d almost made it through the whole contract without having to call — something he’d done only once in the seven years I’d been flying for him. Now he needed his cherries dried and they were especially vulnerable this close to picking time. Even though it hadn’t finished raining there yet, I hopped in the helicopter and flew over.
I landed in a parking lot nearby. The orchard is on Crescent Bar, which is a resort area. Unfortunately, a crack in the Wanapum Dam forced the Grant County Public Utility District (PUD) to drastically reduce water levels to the point where the boat ramp and dock are nowhere near water. This is destroying the summer season for businesses down there, including the condos, shops, restaurants, and rental companies. But it also means that no one will raise an eyebrow if someone lands a helicopter in a parking lot on a Thursday evening in June. In fact, it’s likely to be the most interesting thing anyone down there has seen this season.
I didn’t even have time to shut down. My client saw me and called to get me started.
This is an old orchard with some trees even older than me — can you believe that? The land is somewhat hilly and there’s a house and a shop building inside its boundaries. Also some wires on one end in an odd place. Other than that, no obstacles to speak of. What’s weird, however, is that some rows run east/west while others run north/south. This is a bit of a pain since I follow the aisles between rows. But after drying this orchard at least 10 times over the years, I’d learned a good, efficient pattern.
Unfortunately, my client wanted be to dry in a different order. He called with instructions. I did my best to follow them. The idea was to dry the trees with the most fruit first. Since it takes just over an hour to dry the entire orchard, that made sense, especially with the fruit so vulnerable.

My client took about a dozen photos of me in action over his orchard. Of course, he was on the ground looking up.
While I was flying, my phone reminded me that I was due to have dinner at a friend’s house in an hour. I’d already called to postpone the date; I just hadn’t told Siri.
Down below me in various places, they were preparing for the next day’s pick. Outhouses lined the entrance road. A refrigerated truck trailer was parked at the loading dock. Cherry lugs and picking ladders were placed strategically in the area to be picked first. Cherry bins were laid out on trailers. A handful of swampers were moving around, doing odd jobs.
If you want to learn more about the picking process at this orchard, be sure to check out this video I made a few years ago.
The wind was a real factor in this orchard, too. Although it had been calm when I arrived, when I was about 2/3 done it really kicked up. I could easily see the windy spots — it was where the tops of the trees were moving nowhere near me. The trees in that area were young and I suspected that the wind alone might be enough to shake the water off. But I wasn’t taking chances. I kept flying.
I was very glad when I finished the orchard. I did my usual “victory lap” past the shop to say goodbye. Then it was back to the airport for fuel before making the 3-minute flight home.
More to Come?
The weather looked iffy for the rest of the day and I thought there might be a chance of more rain. So after a snack, I settled down in my La-Z-Boy, still in my flight suit, to relax. It was probably around 8 PM when I fell asleep.
I woke up, shut the door, and went to bed around 11 PM. I’d only flown 1.9 hours; I was clearly out of shape.
Little did I know, but there would be much more to come the next day.